Conditional Random Field (CRF) is the go-to algorithm for sequence labeling problems. Initial attempts at sequence labeling such as POS tagging and Named Entity Recognition were accomplished using the Hidden Markov Models. Although HMMs gave promising results for the same, they suffered from the same drawbacks as using a Naive Bayes models i.e conditional independence.
Both Naive Bayes (and HMM in extension) try to fit a model that maximizes the joint probability distribution P(X , Y). This is flawed on two levels. One, since X is already given, trying to fit a joint distribution over both X and Y is computationally expensive, wasteful and in the end, we do not require the type of distribution the input variable follow. We just need to know what distribution the target variable follows given an input variable. Second, since we are assuming that the input variables are conditionally independent, if there exists some correlation between the variables, the model assigns high probability when these two variables occur together instead of generalizing over the input distribution. Hence, we can see that any perturbance in the input distribution has a significant effect over the output. Ideally, since we only care about the distribution of the target variable Y, this should not be under consideration. We should evaluate P(Y | X) instead of P(X , Y).
In hindsight, this might seem trivial and as the obvious choice for any classification problem. In fact, majority of the classifiers in use today optimize over this metric. Nevertheless, it was an important breakthrough when it was considered decades ago.
A Conditional Random Field (CRF) does exactly this. It evaluates P(Y | X). The purpose of this post is to delve deeper into the mathematics of a CRF and why CRF is considered to be the starting point for most of the current classification algorithms.
Consider a function Q(.) as a real valued function. According to Markovian distribution theorem,
&space;\propto&space;exp(\sum&space;_{c\in&space;C}Q(c,&space;X,Y)))
Where C is a set of feature verticals (or cliques). This equation provides us with the un-normalized joint probability distribution over X and Y. Since we are interested in calculating the conditional probability,
=&space;\frac{exp(\sum&space;_{c\in&space;C}Q(c,&space;X,Y))}{\sum&space;_{X}exp(\sum&space;_{c\in&space;C}Q(c,&space;X,Y))})
This is similar to Gibbs Distribution (or Softmax depending on the Q(.) function)
The above equation can be re written as
=&space;\frac{\prod&space;_{C}\phi&space;_{C}(X,&space;Y)}{Z})
Where&space;=&space;exp(Q(C,X,Y))) and Z is called as the Partition Function.
and Z is called as the Partition Function.
))
For a CRF which is used for sequence labelling such as PoS or NER, the graph forms a linear chain and the probability equation can be written as
&space;=&space;\frac{1}{Z}\prod&space;_{i}\phi&space;(Y_{i},X)\phi^{1}(Y_{i-1},Y_{i},X))
Where,
&space;=&space;exp(\sum&space;_{k}\theta&space;_{k}s_{k}(y_{i},x_{i},i)))
&space;=&space;exp(\sum&space;_{j}\lambda_{j}t_{j}(y_{i-1},y_{i},x_{i},i)))
where sk is the state feature function and tj is the transition feature function (Similar to HMMs).
CRF is a generalized method of calculating P(Y | X) and is not restricted to just evaluating sequence label probabilities. The flexibility of CRFs stems from the ability to choose any function as Q(X , Y). In the following section, we can see how the logistic function can also be derived from CRF.
Consider the feature function,
&space;=&space;exp(w_{i}1(X_{i},Y)))
where 1 is an indicator function. It can also be denoted as&space;=&space;exp(w_{i}*&space;AND(X_{i},Y)))
Calculating the probabilities,
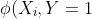&space;=&space;exp(w_{i}X_{i}))
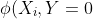&space;=&space;exp(0)=1)
Therefore, substituting the above results in the CRF equation, we get,
&space;=&space;\frac{\phi&space;(X_{i},Y=0)&space;*&space;\phi&space;(X_{i},Y=1)}{\phi&space;(X_{i},Y=0)&space;+&space;\phi&space;(X_{i},Y=1)}&space;=&space;\frac{exp(\sum&space;_{i}w_{i}X_{i})}{1+exp(\sum&space;_{i}w_{i}X_{i})})
The above equation is nothing but the logistic equation. Hence, we can see that CRF is a generalized form of any machine learning classification problem.
Both Naive Bayes (and HMM in extension) try to fit a model that maximizes the joint probability distribution P(X , Y). This is flawed on two levels. One, since X is already given, trying to fit a joint distribution over both X and Y is computationally expensive, wasteful and in the end, we do not require the type of distribution the input variable follow. We just need to know what distribution the target variable follows given an input variable. Second, since we are assuming that the input variables are conditionally independent, if there exists some correlation between the variables, the model assigns high probability when these two variables occur together instead of generalizing over the input distribution. Hence, we can see that any perturbance in the input distribution has a significant effect over the output. Ideally, since we only care about the distribution of the target variable Y, this should not be under consideration. We should evaluate P(Y | X) instead of P(X , Y).
In hindsight, this might seem trivial and as the obvious choice for any classification problem. In fact, majority of the classifiers in use today optimize over this metric. Nevertheless, it was an important breakthrough when it was considered decades ago.
A Conditional Random Field (CRF) does exactly this. It evaluates P(Y | X). The purpose of this post is to delve deeper into the mathematics of a CRF and why CRF is considered to be the starting point for most of the current classification algorithms.
Consider a function Q(.) as a real valued function. According to Markovian distribution theorem,
Where C is a set of feature verticals (or cliques). This equation provides us with the un-normalized joint probability distribution over X and Y. Since we are interested in calculating the conditional probability,
This is similar to Gibbs Distribution (or Softmax depending on the Q(.) function)
The above equation can be re written as
Where
For a CRF which is used for sequence labelling such as PoS or NER, the graph forms a linear chain and the probability equation can be written as
Where,
where sk is the state feature function and tj is the transition feature function (Similar to HMMs).
CRF is a generalized method of calculating P(Y | X) and is not restricted to just evaluating sequence label probabilities. The flexibility of CRFs stems from the ability to choose any function as Q(X , Y). In the following section, we can see how the logistic function can also be derived from CRF.
Consider the feature function,
where 1 is an indicator function. It can also be denoted as
Calculating the probabilities,
Therefore, substituting the above results in the CRF equation, we get,
The above equation is nothing but the logistic equation. Hence, we can see that CRF is a generalized form of any machine learning classification problem.
Leo training is the best institute in Hyderabad
ReplyDeleteExcellent explanation of why CRFs are preferred over HMMs for sequence labeling tasks. Highlighting the shift from modeling joint probability P(X,Y)P(X, Y)P(X,Y) to conditional probability P(Y∣X)P(Y | X)P(Y∣X) really clarifies the conceptual advantage. This post is a great read for anyone trying to understand the limitations of generative models in NLP and the evolution toward discriminative approaches.
ReplyDeleteAI Powered Digital Marketing Course In Hyderabad.
For those looking to achieve a flawless look for any occasion, professional makeup services can make all the difference. I highly recommend checking out the Best Makeup Artists in Hyderabad. With exceptional skills, creativity, and attention to detail, they ensure a stunning transformation that enhances your natural beauty and boosts your confidence.
ReplyDeleteThank you for this insightful guide on Conditional Random Fields (CRFs). Your explanation of CRFs as a framework for structured prediction, particularly in sequence modeling tasks like part-of-speech tagging and named entity recognition, provides a clear understanding of their application. The comparison between CRFs and other models, such as Hidden Markov Models, helps in appreciating the advantages CRFs offer in capturing complex dependencies.
ReplyDeleteAt Fast Prep Academy, we emphasize the importance of mastering advanced machine learning techniques like CRFs to tackle complex prediction problems. Your article serves as an excellent resource for learners aiming to deepen their understanding of these concepts.
"Great explanation of why CRFs are favored over HMMs for sequence labeling tasks. The contrast between modeling the joint probability P(X,Y) and the conditional probability P(Y | X) really highlights the conceptual advantage of CRFs. This post is an excellent read for anyone looking to understand the limitations of generative models in NLP and the shift toward more powerful discriminative approaches."
ReplyDeleteNice explanation — the discussion of conditional random fields was very clear and useful! If anyone also wants to stay on top of studies while doing such technical work, this resource might help: sat coaching online
ReplyDeleteThis post provides an excellent and highly accessible introduction to Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) and their vital role in structured prediction! Highlighting how CRFs overcome the label bias problem found in Hidden Markov Models by using a discriminative approach is a fantastic way to explain their technical superiority. I especially liked the clear breakdown of how they utilize feature functions to model the relationships between observations and labels, making it a perfect resource for anyone working on NLP tasks like named entity recognition or part-of-speech tagging. Just as a precise mathematical model ensures accurate data analysis, specialized medical expertise is vital for health, which is what we prioritize at our Multispeciality Hospital in Kadapa. Thanks for sharing these valuable machine learning insights!
ReplyDeleteImagine trying to teach someone how to drive just by describing a car in a text message. It wouldn’t work. To learn effectively, they need to see the road, understand movement, and hear the engine. AI models are no different. They don’t just “learn”—they learn from specific formats of information provided to them.
ReplyDeleteBut not all data is created equal. The way you label that data changes everything about how your model perceives the world. This is where choosing the right types of data annotation becomes critical. Whether you are building a self-driving car, a voice assistant, or a medical diagnostic tool, feeding your model the wrong type of annotated data can lead to poor performance, wasted budget, and failed deployment.
At the heart of every successful machine learning project lies a less glamorous but absolutely critical process: data annotation. Without it, even the most sophisticated algorithm is just code without a compass. This article explores why data annotation for machine learning is not just a preliminary step, but the very foundation upon which reliable, accurate, and ethical AI is built.
ReplyDeleteData annotator roles and responsibilities are the unsung heroes of the AI revolution. Without the patient, precise work of human annotators, the intelligent systems we rely on—from voice assistants to medical diagnostic tools—would simply not exist.
ReplyDelete